Every project involves uncertainty, tight deadlines and high expectations. That’s where project analysis comes in. By taking a closer look at a project before it begins, during its execution, and after it ends, teams can uncover risks, measure performance and capture valuable insights that lead to better decisions and stronger results on future projects.
What Is Project Analysis?
Project analysis is the process of evaluating a project to assess its viability, performance and outcomes at different stages of the project life cycle. It can be conducted before, during and after a project to ensure alignment with objectives, budgets and stakeholder expectations.
Before a project begins, project analysis often takes the form of a feasibility study, stakeholder analysis or cost-benefit analysis, helping decision-makers determine whether the project is worth pursuing. During execution, it may involve variance analysis, earned value analysis, risk monitoring and other performance assessments that track progress against the original project management plan and its project baseline.
Once a project is completed, project analysis shifts to evaluation methods such as post-mortem meetings and lessons learned documents, which capture successes, challenges and areas for improvement. By applying structured analysis at each stage, organizations gain insights to improve decision-making, optimize resource allocation and enhance future project performance.
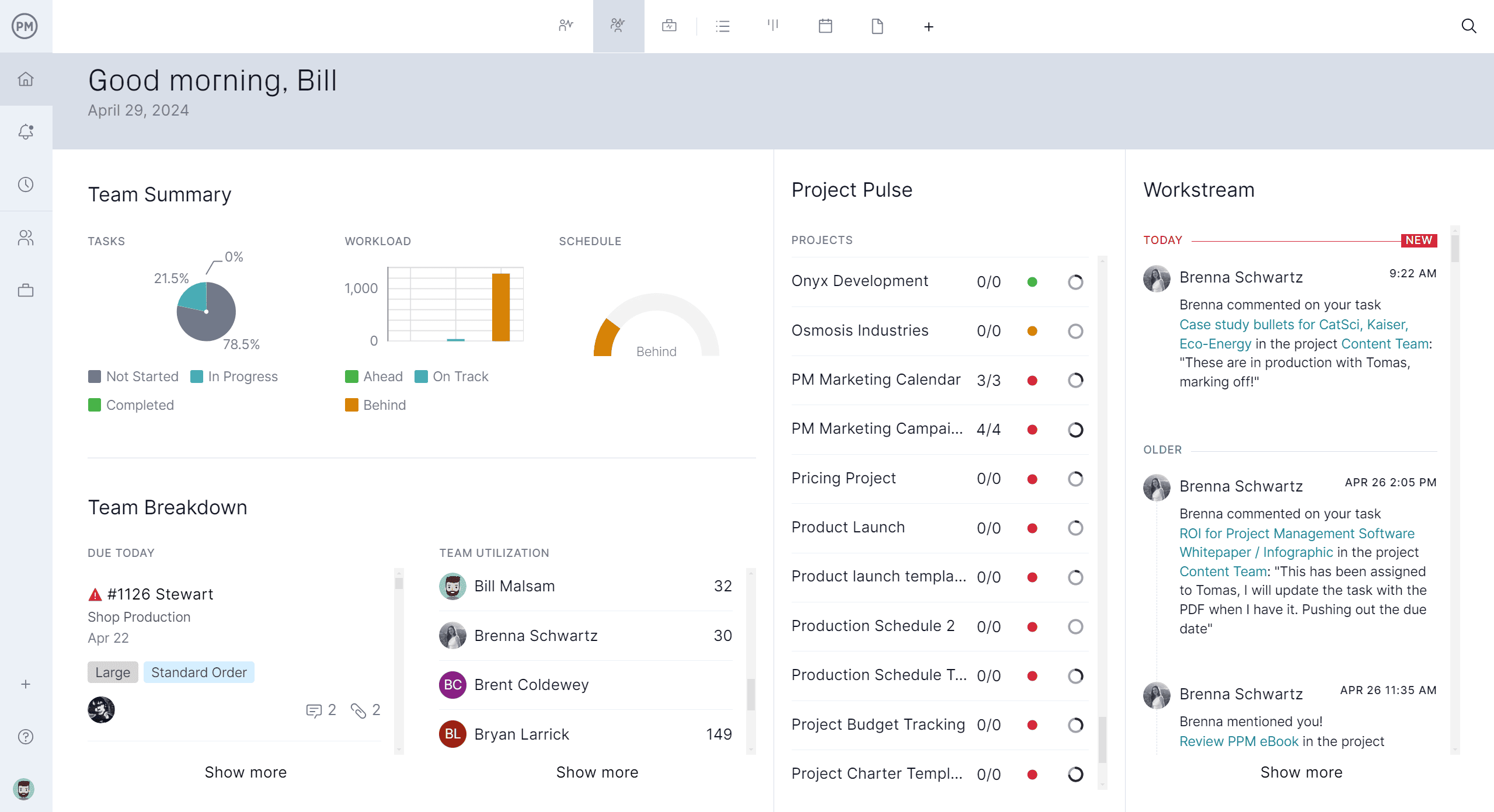
Project management software makes project analysis more effective by centralizing all project data into one accessible platform. Instead of relying on scattered spreadsheets or disconnected reports, managers can evaluate progress, costs and resource allocation in real time. This level of visibility ensures that project analysis is accurate, timely and actionable, allowing teams to identify risks early and make informed decisions that keep projects aligned with goals.
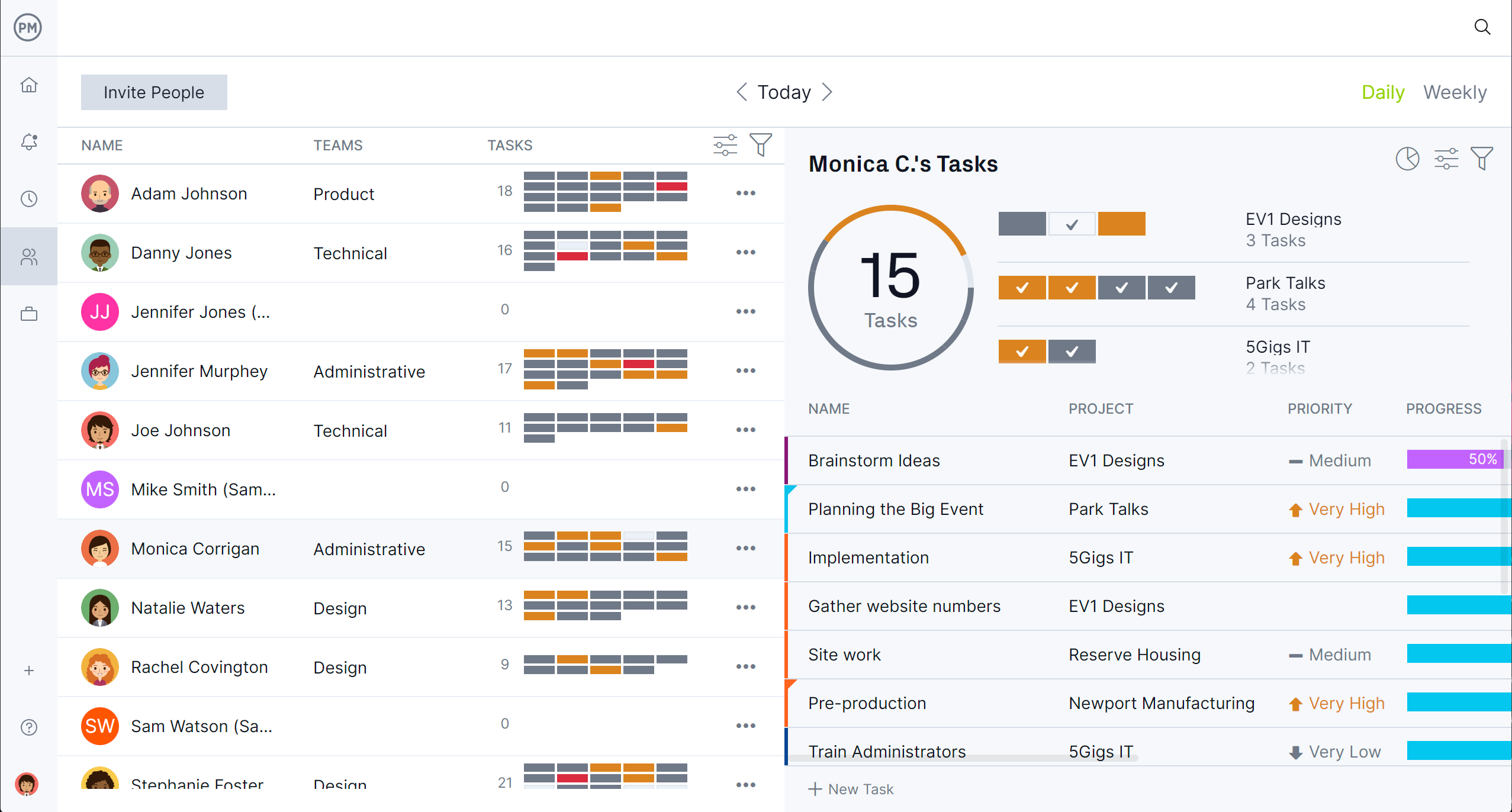
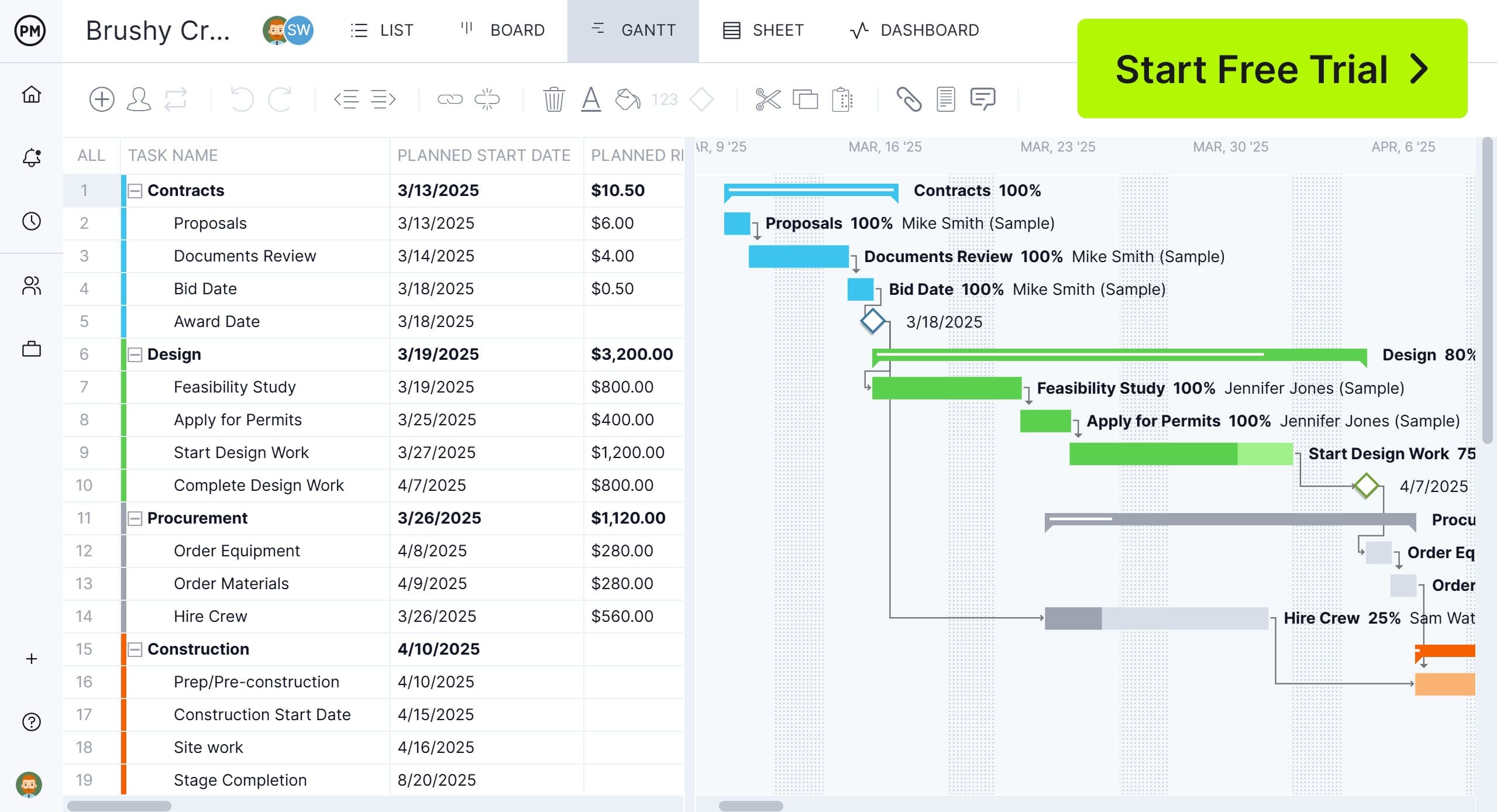
ProjectManager is an ideal tool for project analysis because it combines Gantt charts with powerful reporting and tracking features. The Gantt chart gives managers a clear view of tasks, dependencies and milestones, making it easy to analyze schedules and adjust plans as needed. Beyond that, real-time dashboards, workload management tools and customizable reports provide deeper insights into performance.
With these features working together, ProjectManager simplifies project analysis and ensures teams have the data they need to deliver successful outcomes. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

Why Is Project Analysis Important?
Project analysis is important because it gives managers and teams the insight needed to understand whether a project is progressing as planned. By examining schedules, costs, risks and resources, project analysis highlights potential issues before they become problems. This process ensures that decisions are based on accurate data rather than guesswork, which helps teams stay aligned with goals and stakeholders stay confident in the project’s direction.
Without consistent project analysis, projects are more likely to suffer from delays, budget overruns and misallocated resources. Analyzing performance not only measures current progress but also provides lessons for future initiatives. In this way, project analysis improves efficiency, accountability and overall success across both individual projects and long-term organizational strategies.
Who Is Responsible for Project Analysis?
Project analysis requires collaboration across different roles to ensure that information is accurate and decisions are well-informed. While many team members contribute data and updates, the responsibility for project analysis is usually shared among leadership and oversight positions that guide the project toward successful outcomes.
Project Sponsor
The project sponsor plays a key role in project analysis by reviewing high-level progress and ensuring that the project continues to align with business objectives. Sponsors rely on project analysis to verify that resources are being used effectively and that expected benefits will be delivered. Their involvement helps maintain accountability and secures ongoing support from stakeholders.
Project Manager
The project manager is at the center of project analysis, gathering data on tasks, budgets and risks to evaluate overall performance. They use this analysis to make adjustments, resolve issues and keep the project on track. Because project managers oversee day-to-day execution, they rely heavily on project analysis to make decisions that balance time, cost and quality.
Project Management Office
The project management office (PMO) often provides additional oversight by standardizing how project analysis is conducted across an organization. The PMO ensures consistent reporting, offers tools and guidance and monitors whether projects are delivering value. By supporting both project managers and sponsors, the PMO makes project analysis more reliable and consistent at the organizational level.
Related: Best Project Management Software of 2025 (Comparison List)
When to Execute Project Analysis
Project analysis is a critical step at every stage of a project. Conducting project analysis during initiation, execution and closure ensures objectives are clear, risks are managed and outcomes are evaluated. Regular project analysis helps teams make informed decisions, stay on schedule and continuously improve project performance.
Project Analysis During Project Initiation
Project analysis at the start of a project helps teams define objectives, identify risks and establish clear deliverables. By assessing resources, timelines and stakeholder expectations early, project managers can prevent misalignment and costly mistakes. This initial project analysis ensures that the project has a solid foundation and that everyone involved understands the scope and goals.
Project Analysis During Project Execution
During execution, project analysis monitors progress, identifies issues and evaluates whether the project is on track. Teams can use metrics, dashboards and performance indicators to detect delays or inefficiencies. Continuous project analysis allows managers to adjust resources, revise schedules and implement corrective actions before small problems escalate into major setbacks.
Project Analysis During Project Closure
At closure, project analysis evaluates outcomes against objectives and documents lessons learned. It identifies successes, challenges and areas for improvement that can guide future projects. Conducting thorough project analysis during this phase ensures knowledge transfer and enhances organizational processes for long-term success.
10 Project Analysis Techniques
Project analysis is essential for understanding project performance, identifying risks and ensuring objectives are met. By using the right project analysis techniques at different stages, project managers can make informed decisions, optimize resources and improve outcomes. The following 10 project analysis techniques provide practical methods to assess feasibility, track progress and evaluate results for any type of project.
1. Project Feasibility Analysis
Project feasibility analysis is a key project analysis technique that evaluates whether a project is practical, achievable and worth pursuing before significant resources are committed. It helps managers identify potential barriers, estimate costs and benefits and make informed decisions about moving forward. By conducting a thorough project feasibility analysis, teams reduce the risk of project failure and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
- Technical Feasibility: Assesses whether the technology, tools and systems required for the project are available, suitable and capable of supporting successful implementation. Technical feasibility ensures that project analysis includes the assessment of technology readiness.
- Economic Feasibility: Evaluates the financial viability of a project by analyzing costs, expected returns and potential savings. This ensures the project makes financial sense and aligns with budget constraints, making economic feasibility an important part of project analysis.
- Legal Feasibility: Ensures the project complies with all relevant laws, regulations and contractual obligations. Including legal feasibility in project analysis helps identify potential risks and ensures compliance to prevent legal complications during project execution.
- Operational Feasibility: Examines whether the organization has the capacity, resources and processes to support the project. It evaluates staffing, skills, workflow and management capabilities, making it an integral part of comprehensive project analysis.
- Schedule Feasibility: Evaluates whether the project can be completed within the proposed timeline. Including this in project analysis helps managers determine realistic deadlines, allocate resources effectively and avoid delays that could compromise project success.
2. Project Cost-Benefit Analysis
Project cost-benefit analysis is a core project analysis technique that compares total project costs with anticipated benefits to determine whether the investment is worthwhile. This analysis provides a clear picture of financial trade-offs, helping decision-makers prioritize projects that offer the highest return on investment and strategic value.
Related: Cost-Benefit Analysis Template
3. Project Stakeholder Analysis
Project stakeholder analysis is an important part of project analysis that identifies all individuals, groups and organizations affected by a project. It evaluates their influence, interests and expectations, ensuring the project team engages stakeholders effectively. Understanding stakeholder needs improves communication, reduces conflicts and increases the likelihood of project success.
4. Project Risk Analysis
Project risk analysis is a critical project analysis technique that examines potential threats to project objectives, assessing both likelihood and potential impact. By identifying risks early, managers can develop mitigation strategies, allocate resources proactively and minimize disruptions, ensuring the project stays on track.
5. Project Variance Analysis
Project variance analysis measures differences between planned and actual project performance, such as schedule, cost and scope deviations. By including variance analysis in project analysis, managers can take corrective actions, adjust strategies and maintain control over project outcomes, improving overall project performance.
6. Project Earned Value Analysis
Project earned value analysis is a project analysis technique that tracks progress by comparing planned versus actual costs and work completed. It integrates scope, schedule and cost metrics to provide a comprehensive view of project performance, allowing managers to forecast trends, detect problems early and make informed adjustments.
7. Project Critical Path Analysis
Project critical path analysis identifies the sequence of tasks that determines the shortest possible duration of the project. It highlights tasks that cannot be delayed without affecting the overall schedule. Including this technique in project analysis enables managers to focus on key activities, optimize timelines and prevent bottlenecks.
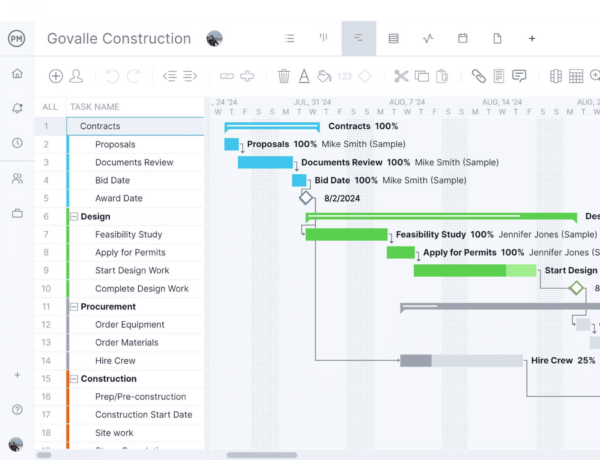

8. Project Profitability Analysis
Project profitability analysis evaluates the financial returns of a project relative to costs. Including profitability analysis in project analysis ensures that projects meet financial targets, support business objectives and justify resource allocation, contributing to overall organizational success.
9. Project Post-Mortem Analysis
Project post-mortem analysis reviews outcomes after project completion to capture lessons learned, identify successes and uncover areas for improvement. Conducting this type of project analysis allows organizations to enhance future project planning, reduce risks and continuously improve project management practices.
10. Project Root Cause Analysis
Project root cause analysis investigates the underlying causes of issues encountered during a project. By including root cause analysis in overall project analysis, teams can implement solutions to prevent recurrence, improve processes and enhance overall project performance for future initiatives.
Free Project Analysis Templates
Project analysis is essential for making informed decisions and keeping projects on track. These free templates provide structured tools to evaluate feasibility, track risks and compare costs and benefits, helping project managers plan and execute projects more effectively.
Cost-Benefit Analysis Template
Download this free template to help you weigh project costs against expected benefits, making it easier to decide whether to proceed with a project. It provides a structured format to list costs, benefits and calculate net value for informed decision-making.
Risk Tracking Template
Use this free risk tracking template to identify, assess and monitor project risks throughout the project lifecycle. It allows project managers to assign ownership, track mitigation actions and ensure risks are addressed proactively.
Feasibility Study Template
The feasibility study template guides you through evaluating a project’s technical, economic, legal, operational and schedule feasibility. It provides a structured approach to determine if the project is viable before committing resources.
How ProjectManager Helps With Project Analysis and Beyond
ProjectManager makes project analysis simpler and more effective by offering multiple project management views. Teams can visualize tasks in Gantt charts, kanban boards or task lists, giving them the flexibility to analyze project progress and identify potential issues early. This approach helps managers optimize resources, maintain schedules and improve overall project analysis across all stages of a project.
Robust Resource Management and Cost Tracking Features
With ProjectManager, teams can assign resources, track workload and monitor costs in real time, enhancing project analysis and budget management. Managers can quickly adjust assignments and allocations based on current data, reducing bottlenecks and ensuring resources are used efficiently. These tools make ongoing project analysis actionable and practical for daily project decisions.
Real-time Project Dashboards and Reports
ProjectManager provides real-time dashboards and customizable reports, giving stakeholders instant insights for better project analysis. Teams can track progress, identify risks and make data-driven decisions quickly. By continuously monitoring metrics, project analysis becomes an integral part of the workflow, enabling continuous improvement and successful project delivery.
Related Project Analysis Content
Want to delve deeper into project analysis? Below are links to some related articles that explain the feasibility study, risk management process and more.
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams, whether they’re in the office or out in the field. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.